Emotional Tendency Analysis of Twitter Data Streams
Main Article Content
Abstract
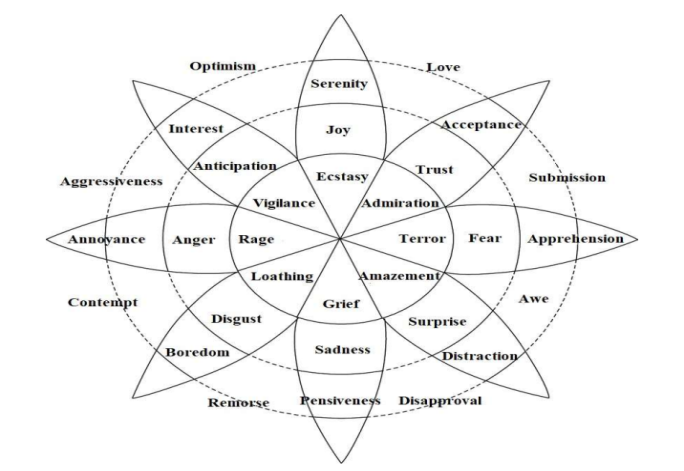
The web now seems to be an alive and dynamic arena in which billions of people across the globe connect, share, publish, and engage in a broad range of everyday activities. Using social media, individuals may connect and communicate with each other at any time and from any location. More than 500 million individuals across the globe post their thoughts and opinions on the internet every day. There is a huge amount of information created from a variety of social media platforms in a variety of formats and languages throughout the globe. Individuals define emotions as powerful feelings directed toward something or someone as a result of internal or external events that have a personal meaning. Emotional recognition in text has several applications in human-computer interface and natural language processing (NLP). Emotion classification has previously been studied using bag-of words classifiers or deep learning methods on static Twitter data. For real-time textual emotion identification, the proposed model combines a mix of keyword-based and learning-based models, as well as a real-time Emotional Tendency Analysis
Article Details
References
Aggarwal, CC, Zhai, C (Eds.), “Mining Text Data”, Springer- Verlag New York, (2012)
Aggarwal, CC, “Opinion Mining and Sentiment Analysis”, In: Machine Learning for Text.Springer, Cham, (2018).
Alex Marin, Bin Zhang and Mari Ostendorf “Detecting Forum Authority Claims in OnlineDiscussions” workshop on language in social media (LSM 2011), page 39-47(23 june2011).
Alom, Z., Carminati, B., & Ferrari, E,”Detecting Spam Accounts on Twitter”. 2018, IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM). doi:10.1109/asonam.2018.8508495.
Angela Fahrni& Manfred Klenner, “Old Wine or Warm Beer: Target-Specific Sentiment Analysis of Adjectives”, Institute of Computational Linguistics, University of Zurich, Switzerland,( 2010).
Anubha Sharma &NirupmaTivari, “A Survey of Association Rule Mining Using GeneticAlgorithm”, International Journal of Computer Applications & InformationTechnology, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 5-11,( 2012).
Apoorv Agarwal, BoyiXie, Ilia Vovsha, Owen Rambow and Rebecca Passonneau“Sentiment Analysis of Twitter Data” workshop on language in social media (LSM 2011), page 30-38(23 june2011).
Bara, I.-A., Fung, C. J., & Dinh, T,”Enhancing Twitter spam accounts discovery using cross- account pattern mining”. 2015 IFIP/IEEE International Symposium on Integrated Network Management (IM). doi:10.1109/inm.2015.7140327.
Bilai, S&Abdelouahab, M, “Evolutionary algorithm and modularity for detecting communities in networks”, Elsevier, vol. 473, pp. 89-96,( 2017).
Cao, D, He, X, Nie, L, Wei, X, Hu, X, Wu, S & Chua, TS, “Cross- platform app recommendation by jointly modeling ratings and texts”, ACM Transactions on Information Systems, vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 1-27,( 2017).
Chao, Y, Robert, H &Guofei, G, “Empirical evaluation and new design for fighting evolving twitter spammers”, IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, vol. 8,no. 8, pp. 1280-1293,(2013).
Chen, J, Nairn, R, Nelson, L, Bernstein, M & Chi, E,”Short and tweet: Experiments on recommending content from information streams”, Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, ACM, pp.1185-1194,(2010).
Chu, Z., Gianvecchio, S., Wang, H., &Jajodia, S., “ Detecting Automation of Twitter Accounts: Are You a Human, Bot, or Cyborg?” IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 9(6), 811–824. doi:10.1109/tdsc.2012.75.
Corcoglioniti, F, Nechaev, Y, Giuliano, C, Zanoli, R, “Twitter user recommendation for gaining followers”, In: Ghidini C., Magnini B., Passerini A., Traverso P. (eds) AI*IA 2018 – Advances in Artificial Intelligence. AI*IA 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 11298. Springer, Cham,( 2018).
Dangkesee, T., &Puntheeranurak, S. “Adaptive Classification for Spam Detection on Twitter with Specific Data”. 2017 21st International Computer Science and Engineering Conference (ICSEC). doi:10.1109/icsec.2017.8443779.
Dong Nguyen and Carolyn P. Rose “Language use as a reflection of socialization in online communities” workshop on language in social media (LSM 2011), page 76-85(23 june2011).
Eshraqi, N., Jalali, M., &Moattar, M. H., “Detecting spam tweets in Twitter using a data stream clustering algorithm”. 2015 International Congress on Technology, Communication and Knowledge (ICTCK). doi:10.1109/ictck.2015.7582694.
EvandroCunha, GabrielMagno, GiovanniComarela, VirgilioAlmeida, MarcosAndr´eGonc¸ alves and FabricioBenevenut,“Analyzing the Dynamic Evolution of Hashtags on Twitter: a Language-Based Approach” workshop on language in social media (LSM 2011), page 58-65(23 june2011).
Ekman, P. (1992). An argument for basic emotions. Cognition and Emotion, 6(3-4), 169–200. doi:10.1080/02699939208411068
Faulkner, A, “Automated classification of stance in student essays: An approach using stance target information and the Wikipedia link- based measure”, In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh International Flairs Conference, 174-179,( 2014).
Feng, Y., Li, J., Jiao, L., & Wu, X., “BotFlowMon: Learning-based, Content-Agnostic Identification of Social Bot Traffic Flows”. 2019 IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security (CNS). doi:10.1109/cns.2019.8802706.
Fulin Wu, Shifei Ding, Huajuan Huang&Zhibin Zhu, “Mixed Kernel Twin Support VectorMachines Based on the Shuffled Frog Leaping Algorithm”, Journal of Computers, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 947-955,( 2014).
Giatsoglou, M, Vozalis, MG, Diamantaras, K, Vakali, A, Sarigiannidis, G &Chatzisavvas, KC, “Sentiment analysis leveraging emotions and word embeddings”, Expert System with Applications, Elsevier, vol. 69, pp. 214-224,( 2017).
Guang Qiu, Bing, Liu, Jaijun Biu & Chun Chen, “Opinion word Expansion and Target Extraction through Double Propagation”, Association of Linguistics, vol. 37, no. 1, pp. 9-27,( 2010).
Guidi, B., &Michienzi, A,”Users and Bots behaviour analysis in Blockchain Social Media”.2020 Seventh International Conference on Social Networks Analysis, Management and Security (SNAMS). doi:10.1109/snams52053.2020.93365.
Gupta, A., & Kaushal, R, “Improving spam detection in Online Social Networks”. 2015 International Conference on Cognitive Computing and Information Processing(CCIP). doi:10.1109/ccip.2015.7100738.
Gupta, H., Jamal, M. S., Madisetty, S., &Desarkar, M. S, “A framework for real-time spam detection in Twitter”. 2018 10th International Conference on Communication Systems & Networks (COMSNETS). doi:10.1109/comsnets.2018.8328222.
Haiying, S & Ze, L, “Leveraging social networks for effective spam filtering”, IEEETransactions on Computers, vol. 63, no. 11, pp. 2743-2759,( 2014).
Tuama, B. A. . (2023). Bigdata Based Disaster Monitoring of Satellite Image Processing Using Progressive Image Classification Algorithm . International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications in Engineering, 11(4s), 70–77. Retrieved from https://ijisae.org/index.php/IJISAE/article/view/2573.
Han, J, Kamber, M & Pei, J, “Data mining: Concepts and techniques”, 3rd ed. Boston: Morgan Kaufmann. J Han, J Pei, M Kamber,( 2012).
Hercig, T, Krejzl, P, Hourová, B, Steinberger, J &Lenc, L, “Detecting stance in czech news commentaries”, In: Proceedings of the 17th ITAT: CEUR Workshop, pp. 176 – 180,(2015).
Heredia, B., Prusa, J. D., &Khoshgoftaar, T. M,”The Impact of Malicious Accounts on Political Tweet Sentiment”. 2018 IEEE 4th International Conference on Collaboration and Internet Computing (CIC). doi:10.1109/cic.2018.00035.
Huang, Z & Cardenas AF, “Extracting Hot Events From New Feeds Visualization and Insights”, in Distributed Multimedia Systems Conference, pp. 10-12,(2009).
Huberman, BA, Romero, DM & Wu, F, “Social networks that matter: Twitter under the microscope”, available at SSRN 1313405,(2008).
Ilias, L., &Roussaki, I., “Detecting malicious activity in Twitter using deep learning techniques”, Applied Soft Computing, 107, 107360. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107360.
Ismaila, I & Ali, S, “Improved email spam detection model with negative selection algorithm and particle swarm optimization”, Elsevier journal of Applied Soft Computing, vol. 22, pp. 11-27,(2014).
Ismaila, I, Ali, S &Sigeru, O, “Hybrid email spam detection model with negative selection algorithm and differential evolution”, Elsevier journal of Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, vol. 28, pp. 97-118,(2014).
Jain, VK, Kumar, S & Fernandes, SL, “Extraction of emotions from multilingual text using intelligent text processing and computational linguistics”, Journal of Computational Science, vol. 21, pp. 316-326,(2017).
Jennifer Golbeck, J, “Introduction to social media investigation: A hands-on approach”, Elsevier,( 2015).
Jiménez-Bravo, DM, De Paz, JF &Villarrubia, G, “Twitter’s experts recommendation system based on user content. In: Rodríguez S. et al. (eds) Distributed Computing and Artificial Intelligence”, Special Sessions, 15th International Conference DCAI 2018. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol. 801. Springer, Cham,( 2019).
Kamble, S., &Sangve, S. M, “Real Time Detection of Drifted Twitter Spam Based on Statistical Features”. 2018 International Conference on Information , Communication, Engineering and Technology (ICICET). doi:10.1109/icicet.2018.8533767.
Mr. Bhushan Bandre, Ms. Rashmi Khalatkar. (2015). Impact of Data Mining Technique in Education Institutions. International Journal of New Practices in Management and Engineering, 4(02), 01 - 07. Retrieved from http://ijnpme.org/index.php/IJNPME/article/view/35.
Kantepe, M., &Ganiz, M. C., “ Pre-processing framework for Twitter bot detection”, 2017 International Conference on Computer Science and Engineering (UBMK). doi:10.1109/ubmk.2017.8093483.
Latah, M., “Detection of Malicious Social Bots: A Survey and a Refined Taxonomy. Expert Systems with Applications”, 113383. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113383,(2020).
Li, Bryan, Dimitrios Dimitriadis& Andreas Stolcke, “Acoustic and Lexical Sentiment Analysis for Customer Service Calls”, ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). IEEE,(2019).
Lingam, G., Rout, R. R., &Somayajulu, D, “Detection of Social Botnet using a Trust Modelbased on Spam Content in Twitter Network”. 2018 IEEE 13th International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems (ICIIS). doi:10.1109/iciinfs.2018.8721318.
Lingam, G., Rout, R. R., &Somayajulu, D., “Deep Q-Learning and Particle Swarm Optimization for Bot Detection in Online Social Networks”. 2019 10th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT). doi:10.1109/icccnt45670.2019.8944.
Madisetty, S., &Desarkar, M. S., “A Neural Network-Based Ensemble Approach for Spam Detection in Twitter”. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 1–12. doi:10.1109/tcss.2018.2878852.
Neha Upadhyay, Angad Singh &NorlelaSamsudin, “A Survey on Twitter for Sentimental Analysis using Machine Learning Methods”, vol.6, no. 5, pp. 4890-4893,( 2016).
Okamoto, M & Kikuchi, M, “Discovering volatile events in your neighborhood: Local-area topic extraction from blog entries”, in Asia information Retrieval Symposium, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, p. 181-192.
Wartena, C&Brussee, R 2008, ‘Topic Detection by Clustering Keywords’, Database and Expert Systems Application, DEXA’08.19th International Workshop on IEEE, pp. 54-58,( 2009).
Pio Sajin, R. Ashwini, B. Baron Sam, “Distributed and Improvised Up-GrowthApproachfor Utility Based Mining” Research India Publications, (2015).
Praveen Kumar Rajendran, A. Asbern, K. Manoj Kumar, M. Rajesh, R.Abhilash. "Implementation and analysis of Map Reduce on biomedical bigdata. "Indian Journal of Science and Technology 9.31,(2016).
Rahman, M. A., Zaman, N., Asyhari, A. T., Sadat, S. M. N., Pillai, P., &Arshah, R. A., “SPY-BOT: Machine learning-enabled post filtering for Social Network-Integrated Industrial Internet of Things”, Ad Hoc Networks, 121, 102588. doi:10.1016/j.adhoc.2021.102588.
Rajiv Bajpaiet, “Aspect-Sentiment Embeddings for Company Profiling and Employee Opinion Mining Computation and language”,( 2019).
RamnathBalasubramanyan, William W. Cohen, Doug Pierce and David P. Redlawsk “What pushes their buttons? Predicting comment polarity from the content of political blog posts” workshop on language in social media (LSM 2011), page 12-19(23 june2011).
Rob Abbott, Marilyn Walker, Pranav Anand, Jean E. Fox Tree, Robeson Bowmani and Joseph King “How can you say such things?!?: Recognizing Disagreement in Informal Political Argument” workshop on language in social media (LSM 2011), page 2-11(23 june2011).
Rodríguez, FM, Torres, LM & Garza, SE, “Followee recommendation in Twitterusing fuzzy link prediction”, Expert Systems, vol. 33, no. 4, pp. 349-361,( 2016).
Maria Gonzalez, Machine Learning for Anomaly Detection in Network Security , Machine Learning Applications Conference Proceedings, Vol 1 2021.
Rohan, A, Julie, R &Johanvan, D, “Detecting targeted malicious email”, IEEE Transactions on Computer and Security, vol.10, no. 3, pp. 64-71,( 2012).
Sahoo, S. R., & Gupta, B. B., “Hybrid approach for detection of malicious profiles in twitter.Computers & Electrical Engineering”, 76, 65–81. doi:10.1016/j.compeleceng.2019.03.
Samaneh Moghaddam & Fred Popowich, “Opinion Polarity Identification through Adjectives”, Computation and Language, Cornell University, (2010).
Sedhai, S., & Sun, A., “Semi-Supervised Spam Detection in Twitter Stream. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems”, 5(1), 169–175. doi:10.1109/tcss.2017.2773581.
Gyawali, M. Y. P. ., Angurala, D. M. ., & Bala, D. M. . (2020). Cloud Blockchain Based Data Sharing by Secure Key Cryptographic Techniques with Internet of Things. Research Journal of Computer Systems and Engineering, 1(2), 07:12. Retrieved from https://technicaljournals.org/RJCSE/index.php/journal/article/view/5.
Shetty, G., Nair, A., Vishwanath, P., &Stuti, A, “Sentiment Analysis and Classification on Twitter Spam Account Dataset”, 2020 Advanced Computing and Communication Technologies for High Performance Applications (ACCTHPA). doi:10.1109/accthpa49271.2020.921.
Shi, P., Zhang, Z., & Choo, K.-K. R., “Detecting Malicious Social Bots based on Clickstream Sequences”. IEEE Access, 1–1. doi:10.1109/access.2019.2901864.
Shoukry, A &Rafea, A, “Preprocessing Egyptian Dialect Tweets for Sentiment Mining”, the Fourth Workshop on Computational Approaches to Arabic Script-based Languages. AMTA2012, San Diego, CA USA,(2012).
Sinha, P., Maini, O., Malik, G., & Kaushal, R, “Ecosystem of spamming on Twitter: Analysis of spam reporters and spam reportees”. 2016 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI). doi:10.1109/icacci.2016.7732293.
Sobhani, P, Inkpen, D &Matwin, S, “From argumentation mining to distance classification”, In: Proceedings of the Workshop on Argumentation Mining, pp. 67–77,( 2015).
Stephan Gouws, Donald Metzler, Congxing Cai and Eduard Hovy “Contextual Bearing on Linguistic Variation in Social Media” workshop on language in social media (LSM 2011), page 20-29(23 june2011).
Szde Yu, “Covert communication by means of email spam: A challenge for digital investigation”, Elsevier journal on Digital Investigation, vol. 13, pp. 72-79,( 2015).
Tingmin Wu, Shigang Liu, Jun Zhang and Yang Xiang, “Twitter Spam Detection based on Deep Learning”,ACSW 17, January 31-February 03, 2017, Geelong, Australia.
Tran, VC, Hwang, D, Nguyen, NT, “Hashtag recommendation approach based on content and user characteristics”, Cybernetics and Systems, vol. 49, no. 5, pp. 368-383,( 2018).
Treeratpituk, P & Callan, J, “Automatically labelling hierarchical clusters”, in Proceedings of the 2006 international conference on Digital government research, Digital Government Society of North America, pp. 167-176.
Velavan, P &Subashini, S, “Correlation Based Feature Selection with Irrelevant Feature Removal”, International Journal on Computer Science and Mobile Computing, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 862-867,( 2014).
Walaa Medhat, Ahmed Hassan, B & Hoda Korashy, “Sentimental Analysis Algorithms and Applications: A Survey”, Ain Shams Engineering Journal, vol. 5, pp. 1093-1113,( 2014).
Wang, X., Kang, Q., An, J., & Zhou, M. , “Drifted Twitter Spam Classification using Multiscale Detection Test on K-L Divergence”. IEEE Access, 1–1. doi:10.1109/access.2019.2932018.
Wei, F., & Nguyen, U. T., “ Twitter Bot Detection Using Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Neural Networks and Word Embeddings”. 2019 First IEEE International Conference on Trust, Privacy and Security in Intelligent Systems and Applications (TPS-ISA). doi:10.1109/tps-isa48467.2019.00021.
Wu, B., Liu, L., Yang, Y., Zheng, K., & Wang, X, “Using Improved Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks to Detect Social Bots on Twitter”. IEEE Access, 8, 36664–36680. doi:10.1109/access.2020.2975630.
Wu, Y., Fang, Y., Shang, S., Jin, J., Wei, L., & Wang, H, “A novel framework for detecting social bots with deep neural networks and active learning”. Knowledge-Based Systems, 211, 106525. doi:10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106525.
Xianghan, Z, Zhipeng, Z, Zheyi, C, Yuanlong, Y &Chunming, R, “Detecting spammers on social networks”, Elsevier Journal on Neurocomputing, vol. 159, pp. 27-34,( 2015).
Xu, Y, Quan, G, Xu, Z & Wang, Y, “Research on Text Hierarchical Topic Identification Algorithm Based on the Dynamic Diverse Thresholds Clustering”, Conference on Asian Language Processing, pp. 206-210,( 2009).
Zappavigna, M, “Enacting identity in microblogging through ambient affiliation”, Discourse &Communication,vol. 8, pp. 209–228,( 2014).
Zhang, Lei, Shuai Wang & Bing Liu, “Deep learning for sentiment analysis: A survey”,WileyInterdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery vol. 8.4, pp.