Heart Disease Prediction Using Ensemble Model and Hyperparameter Optimization
Main Article Content
Abstract
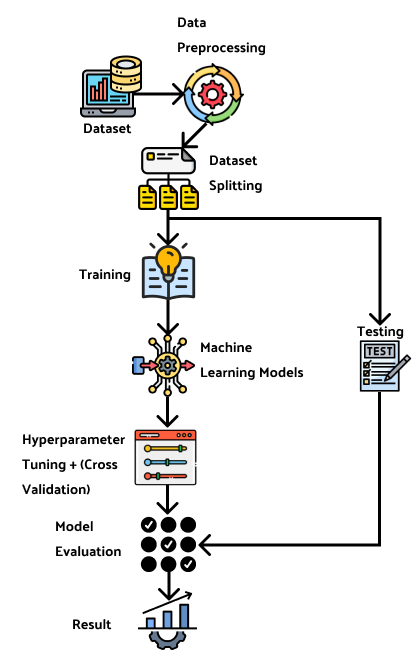
Heart disease is a major global health concern that responsible for significant mortality rates, killing 17.9 million people each year on average. To overcome this problem, machine learning can assist in forecasting the occurrence of heart disease, aiding in its prevention and treatment. This paper explores several classification models to forecast heart disease. This paper also utilizes the hyperparameter tuning method via grid search cv to enhance the accuracy of the models. Finally, the experiment concludes with an ensemble vote on all hyperparameter-tuned classification models. The x-gradient boost and random forest classifier deliver the best outcomes, with an accuracy of 88.04% and 89.13% before hyperparameter optimization, and 92.39% after hyperparameter optimization. These results show that machine learning models are capable of forecasting the risk of heart disease. These models may assist healthcare professionals in identifying individuals at risk of heart disease, enabling preventative measures to be taken. It is essential to note that this study focuses solely on classification models and may not represent the entire population. Further research is required to determine the predictability of heart disease in diverse populations.
Article Details
References
WHO, “Cardiovascular diseases.” Accessed: Apr. 12, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases#tab=tab_1
C. B. C. Latha and S. C. Jeeva, “Improving the accuracy of prediction of heart disease risk based on ensemble classification techniques,” Inform Med Unlocked, vol. 16, Jan. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2019.100203.
J. P. Li, A. U. Haq, S. U. Din, J. Khan, A. Khan, and A. Saboor, “Heart Disease Identification Method Using Machine Learning Classification in E-Healthcare,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 107562–107582, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3001149.
S. Mohan, C. Thirumalai, and G. Srivastava, “Effective heart disease prediction using hybrid machine learning techniques,” IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 81542–81554, 2019, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2923707.
P. Puvar, N. Patel, A. Shah, R. Solanki, and D. Rana, “Heart Disease Detection using Ensemble Learning Approach,” International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2021, [Online]. Available: www.irjet.net
P. Gupta and D. D. Seth, “Improving the Prediction of Heart Disease Using Ensemble Learning and Feature Selection,” International Journal of Advances in Soft Computing and its Applications, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 36–48, 2022, doi: 10.15849/IJASCA.220720.03.
P. Premananthan, S. Prasanth, and K. Mauran, “HYPER PARAMETER TUNED ENSEMBLE APPROACH FOR HEART DISEASE PREDICTION.”
K. Rohit Chowdary, P. Bhargav, N. Nikhil, K. Varun, and D. Jayanthi, “Early heart disease prediction using ensemble learning techniques,” in Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Institute of Physics, 2022. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2325/1/012051.
David W. Aha, “Heart Failure Prediction Dataset,” Kaggle. https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/fedesoriano/heart-failure-prediction (accessed Apr. 12, 2023).
N. Ahmed et al., “Machine learning based diabetes prediction and development of smart web application,” International Journal of Cognitive Computing in Engineering, vol. 2, pp. 229–241, Jun. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.ijcce.2021.12.001.
M. M. Ali, B. K. Paul, K. Ahmed, F. M. Bui, J. M. W. Quinn, and M. A. Moni, “Heart disease prediction using supervised machine learning algorithms: Performance analysis and comparison,” Comput Biol Med, vol. 136, Sep. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104672.
R. Katarya and S. K. Meena, “Machine Learning Techniques for Heart Disease Prediction: A Comparative Study and Analysis,” Health Technol (Berl), vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 87–97, Jan. 2021, doi: 10.1007/s12553-020-00505-7.
P. Anbuselvan, “Heart Disease Prediction using Machine Learning Techniques.” [Online]. Available: www.ijert.org
R. Kannan and V. Vasanthi, “Machine learning algorithms with ROC curve for predicting and diagnosing the heart disease,” in SpringerBriefs in Applied Sciences and Technology, Springer Verlag, 2019, pp. 63–72. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-0059-2_8.
R. Valarmathi and T. Sheela, “Heart disease prediction using hyper parameter optimization (HPO) tuning,” Biomed Signal Process Control, vol. 70, Sep. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103033.
K. Budholiya, S. K. Shrivastava, and V. Sharma, “An optimized XGBoost based diagnostic system for effective prediction of heart disease,” Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, vol. 34, no. 7, pp. 4514–4523, Jul. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.jksuci.2020.10.013.
I. D. Mienye, Y. Sun, and Z. Wang, “An improved ensemble learning approach for the prediction of heart disease risk,” Inform Med Unlocked, vol. 20, Jan. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2020.100402.
S. Y. Prasetyo, “Prediksi Gagal Jantung Menggunakan Artificial Neural Network,” Jurnal SAINTEKOM, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 79–88, Mar. 2023, doi: 10.33020/saintekom.v13i1.379.