GPU Accelerated Simulation of Scene Generation of 3D Photonic Mixer Device Camera
Main Article Content
Abstract
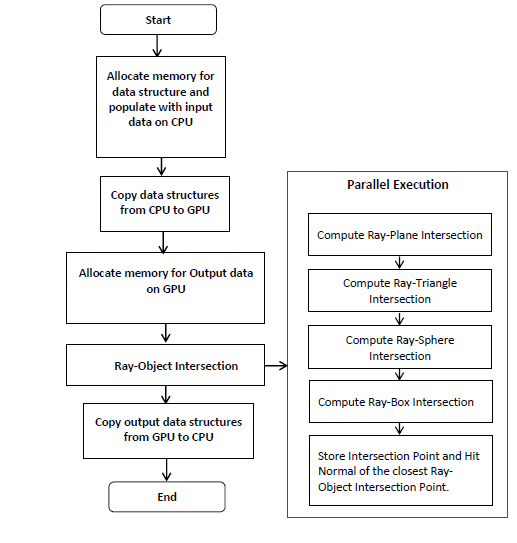
Simulation of Photonic Mixer Device (PMD) sensors have the capability to create virtual environment to test 3D camera design. This simulation comprises of multiple steps like scene generation using ray tracing, power calculation, raw data generation and raw data processing. However, each step-in situation process takes longer time to implement and they are simulation process, simulators need to be faster. In this paper, we propose parallel implementation method for scene generation using GPGPUs. The feasibility of the method is confirmed using Amdahl’s law before implementation. The method is implemented and tested on GeForce 820M, GeForce 750Ti and Volta V100.Tthe highest speed up obtained is 219.913 using Volta (GV100) GPU for block size 1024. Thus, parallel method optimizes the scene generation time as compared to serial processing and the implemented results are better than the state of the art in the literature.
Article Details
References
Lade, S., Kulkarni, M., Patil, A. Ray Tracing Algorithm for Scene Generation in Simulation of Photonic Mixer Device Sensors. In: Swain, D., Pattnaik, P.K., Athawale, T. (eds) Machine Learning and Information Processing. Advances in Intelligent Systems and
Computing. 2021; vol 1311. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-4859-2_25
Timothy L. Kay James T. Kajiya. Ray Tracing Complex Scenes. California Institute of Technology, © 1986; A CM 0-89791-196-2/86/008/0269
Sayed Ahmadreza Raziana, Hossein Mahvash Mohammadi. Optimizing Raytracing Algorithm Using CUDA. Italian Journal of Science and Engineering. October, 2017; Vol. 1, No. 3, http://www.ijournalse.org/
Timothy J. Purcell, Ian Buck, William R. Mark, and Pat Hanrahan. Ray tracing on programmable graphics hardware. 2002; In Proc. SIGGRAPH.
Hussain Bukhari, S. N. . (2021). Data Mining in Product Cycle Prediction of Company Mergers . International Journal of New Practices in Management and Engineering, 10(03), 01–05. https://doi.org/10.17762/ijnpme.v10i03.127
Nathan A. Carr, Jesse D. Hall, and John C. Hart. The ray engine. In Proc. Graphics Hardware Sep 2002; pages 37–46.
Vlastimil Havran. Heuristic Ray Shooting Algorithms. Ph.d. thesis, Dept. of CSE, Fac. of EE, Czech Technical University in Prague, Nov. 2000.
Wald, I., Boulos, S., and Shirley, P. Ray tracing deformable scenes using dynamic bounding volume hierarchies. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 1, Article 6. January 2007; 18 pages. DOI=10.1145/1186644.1186650 http://doi.acm.org/ 10.1145/1186644.1186650
Matt Pharr, Craig Kolb, Reid Gershbein and Pat Hanraha. Rendering Complex Scenes with Memory-Coherent Ray Tracing. Association for Computing Machinery, Inc.1997
Pitkin, Thomas A. GPU ray tracing with CUDA. EWU Masters Thesis Collection. (2013); 94. http://dc.ewu.edu/theses/9
Liang Chen Hirakendu Das Shengjun Pan. An Implementation of Ray Tracing in CUDA CSE 260 Project Report. December 4, 2009
Dhruv Dhote, Charu Virmani, Gopi Krishna, Shivansh Raghav. The Science of Ray Tracing. International Journal of Computer Applications (0975 – 8887). July 2020; Volume 176 – No. 42.